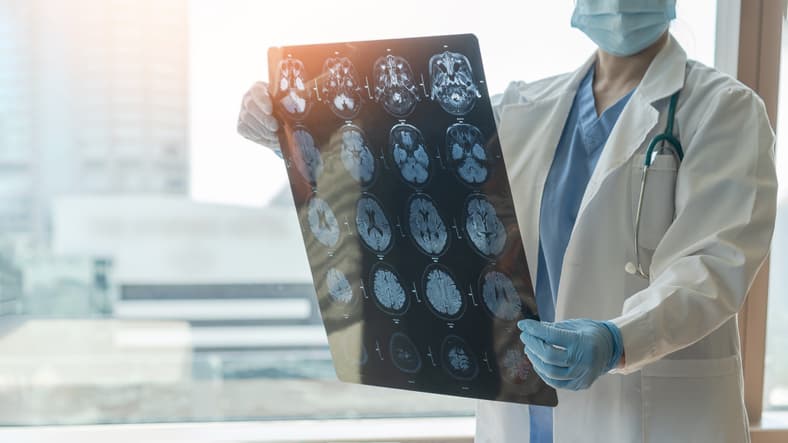
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a type of ischemic stroke that should be considered a warning sign that could eventually lead to a stroke. Strokes occur due to a blood clot that stops blood flow to the brain and can result in mobility issues, speech impediments, and brain damage.
What is a transient ischemic attack (TIA)?
A TIA is often diagnosed as a mini-stroke because its effects are only short-lived. The symptoms are similar to a regular stroke, but it only lasts a few minutes but not more than a day. TIAs often proceed a regular stroke, so should you or someone you care about experience a TIA, it is essential to seek immediate medical care.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) occurs when:
- The blood flow to the brain has been disrupted due to a blockage or blood clot.
- The blood vessels are injured in some manner.
- A narrowing of the arteries or blood vessels causes the blockage.
- Oxygen is not able to get to the brain.
The blockage or clog usually clears quickly, so the effects of the TIA diminish fairly quickly.
What are the effects of a TIA stroke?
The effects of a TIA stroke mimic those of a regular stroke, including:
- Weakness or numbness to the arm, legs, and face.
- Difficulties speaking and forming speech sounds.
- Visual problems with difficulties focusing.
- Mobility and coordination problems.
- Loss of muscle control.
The effects experienced can vary, and some people may not even realize they have had a TIA.
Do you think you had a TIA? Get a heart or body scan today to help identify potential risk factors that could lead to future TIAs and strokes.
How long does a transient ischemic attack last?
Usually, a transient ischemic attack only lasts for a few minutes. Once the blockage is no longer present, blood flow and oxygen supply are restored. In some cases, the effects of a TIA are not even noticed as they may seem minor.
What causes the stroke-like symptoms of a TIA to disappear?
The blockage that triggered the TIA quickly dissolves and breaks up without medical intervention. As a result, the lack of oxygen to the brain is not sufficient to cause brain damage. As the blockage clears, blood flow returns to normal, and the symptoms of TIA disappear.
What are some common risks of having TIAs?
There are some common medical conditions that could increase the risks of having TIAs, including:
- High Cholesterol
- High Blood Pressure
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Abnormal Blood Clotting
- Poor Blood Circulation
In most cases, these are conditions that you can control and manage to lower your risks. However, there are also other risks you need to be aware of, such as:
- Family History
- Age
- Being a Male
- Illicit Drug Use
- Smoking
- Alcohol Use
- Ethnicity
How can I tell if I am having a TIA?
How to diagnose a TIA mini stroke requires knowing that the primary symptoms of TIAs are the same as a stroke. To determine if you are having or have had a TIA, remember this simple acronym: FAST.
- F – The face can drop on one side and be uneven when you smile.
- A – The arms can feel numb or weak, and it can be difficult to raise them.
- S – The speech can seem slurred, or you may not be able to form words at all. You may not even understand what others are saying to you.
- T – If you experience any of these symptoms, it is time to seek immediate medical attention.
What is the difference between a stroke and TIA?
The primary difference between a stroke and TIA is that the blockage or blood clot cannot dissolve on its own without medical intervention. Instead, it remains in place, and every minute counts. The longer a stroke lasts, the more likely there is to be permanent brain damage.
According to CBD Health, a stroke can last up to ten hours. The longer you wait to seek medical treatment, the more brain cells will die. Should a stroke go untreated for a ten-hour period, the brain will age as much as 36 years. Furthermore, two million brain cells die every minute a stroke goes untreated.
How can I avoid a stroke after a TIA?
TIAs are essentially your body’s way of warning you that you will most likely have a future stroke. According to the American Heart Association, about 15% of all strokes were preceded by TIAs.
Additionally, between 7% and 40% report they experienced TIAs before having an ischemic stroke. Most importantly, about 33% of those that have had a TIA will have a stroke within a year.
The best way how to avoid stroke after TIA is by making lifestyle choice changes. If you smoke, drink, or use drugs, get help quitting. If you are obese, consult a nutritionist about developing a healthy diet plan. It would help if you also started a supervised exercise regimen with a personal trainer.
You should also visit your doctor and obtain a referral for a heart scan and body scan to determine the health of your circulatory system. These scans can help pinpoint areas where there is excess buildup inside arteries and blood vessels that could trigger a TIA or stroke.
In Las Vegas, you can get your body scan or heart scan at Preventative Diagnostic Center. We are the premier, leading, non-invasive full-body scan diagnostic facility in the Las Vegas area. You also do not need a referral to schedule your scan.
Are you at risk for TIA, or have had a TIA? Schedule a heart or body scan today to help reduce the risks for a stroke.
Sources:
FAST Signs of a Stroke. (2021).
What Happens When a Stroke Goes Untreated? (2021).
What Is a TIA? (2018).